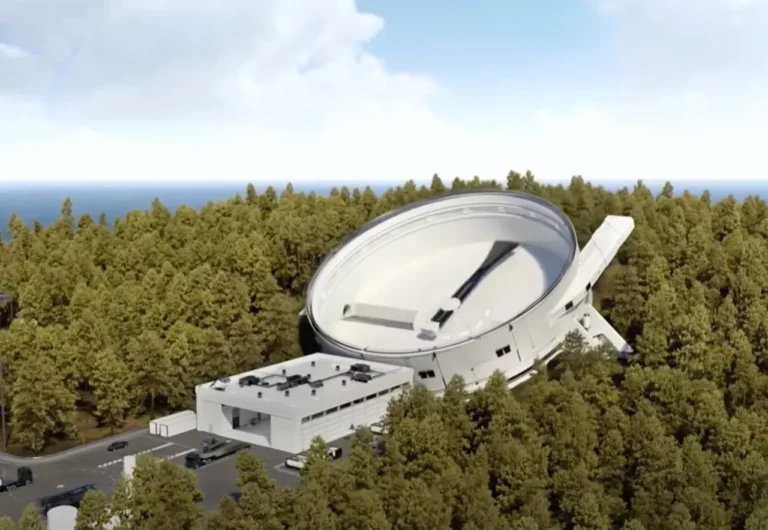
The California -based company, SpinLaunch, has created waves with an innovative satellite launch system and attracts something particularly interesting from the Punkin Chunkin community.
SpinLaunkh uses a huge rotating arm to promote satellites on low -global tracks, which are powered by electricity alone, instead of relying on conventional rocket fuel. This approach can significantly reduce the cost and environment of satellite launch.
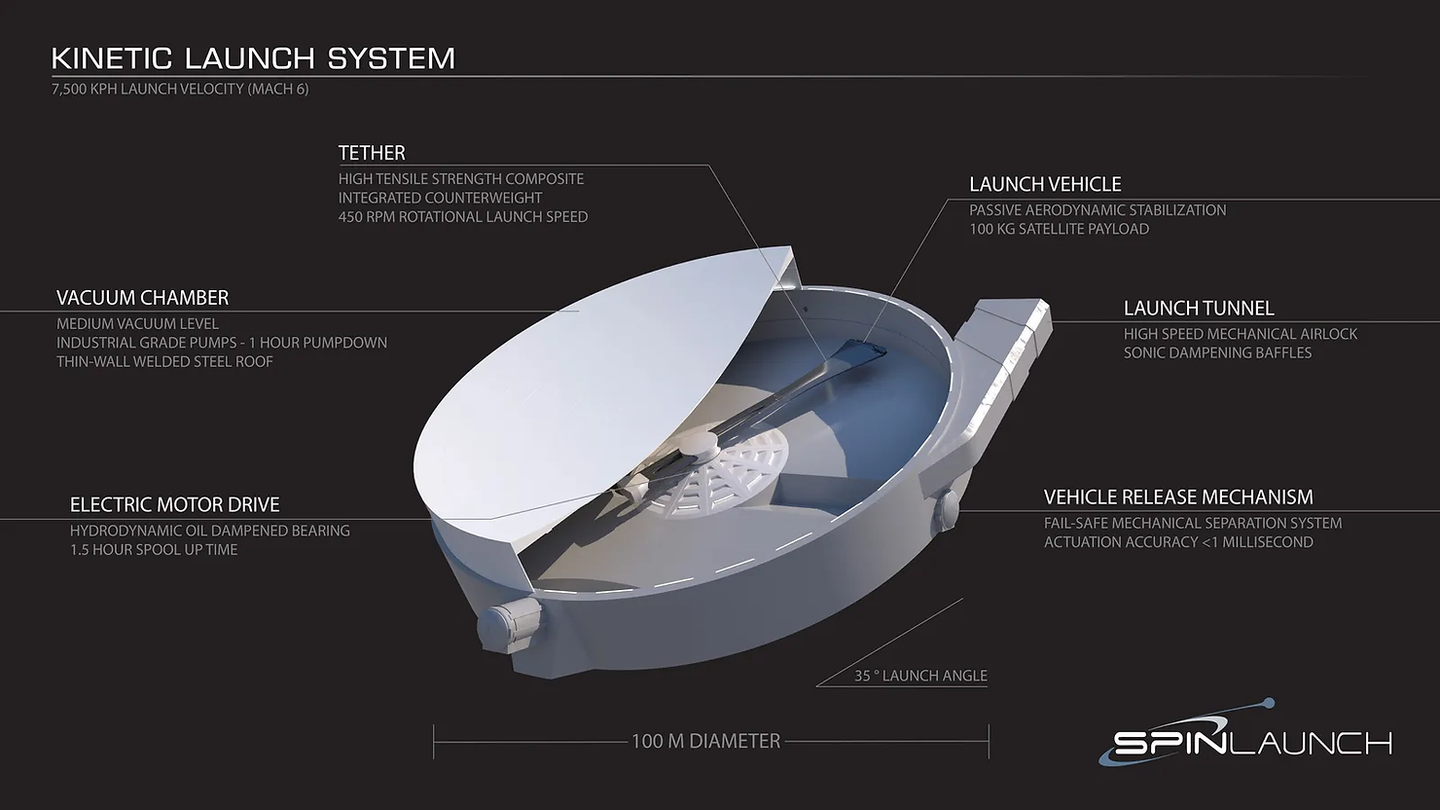
The company has already completed several successful test flights. “This is not a rocket. Obviously, it is a proof of our technology to perform this many tests in just 11 months and to function as planned.” SpinLaunch aims to expand the satellite constellation in a track of less than 600 miles by 2026.
The satellite plays an important role in monitoring the health of the earth, detecting methane leaks, and supporting various scientific efforts. More clean and efficient launch systems can move these functions while reducing traditional dependence on rocket promotion.
The concept of SpinLaunch is revolutionary in modern space flight, but the basic physics dates back to centuries. The medieval siege engine, such as a trevute chet, also used a kinetic energy to throw heavy objects over long distances.
The modern Pankin Chunkin Contest will launch pumpkins using similar mechanisms, show off speed -based energy, and present potential energy in action. SPINLAUNCH systems may be wondering how much pumpkin can be sent to space with such a machine.
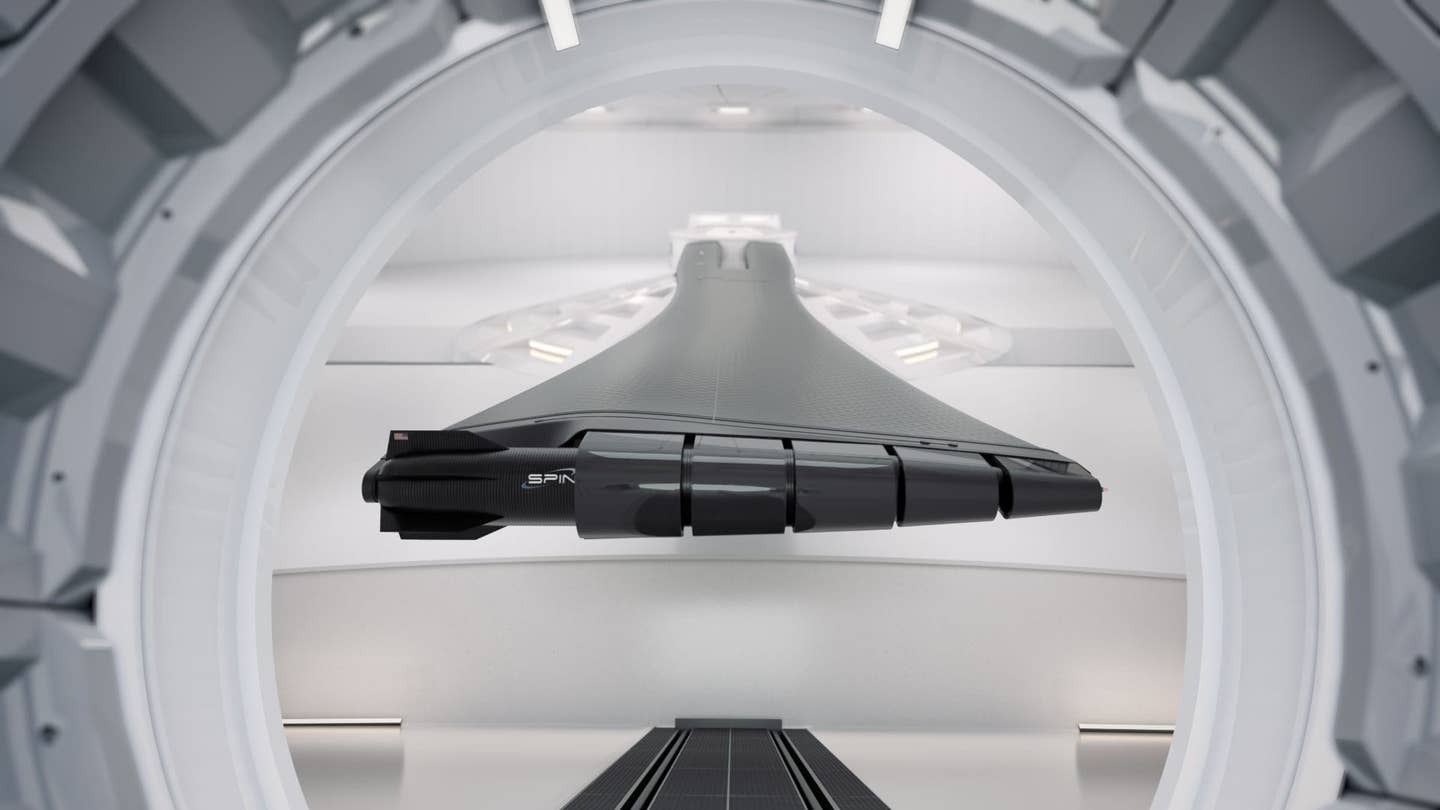
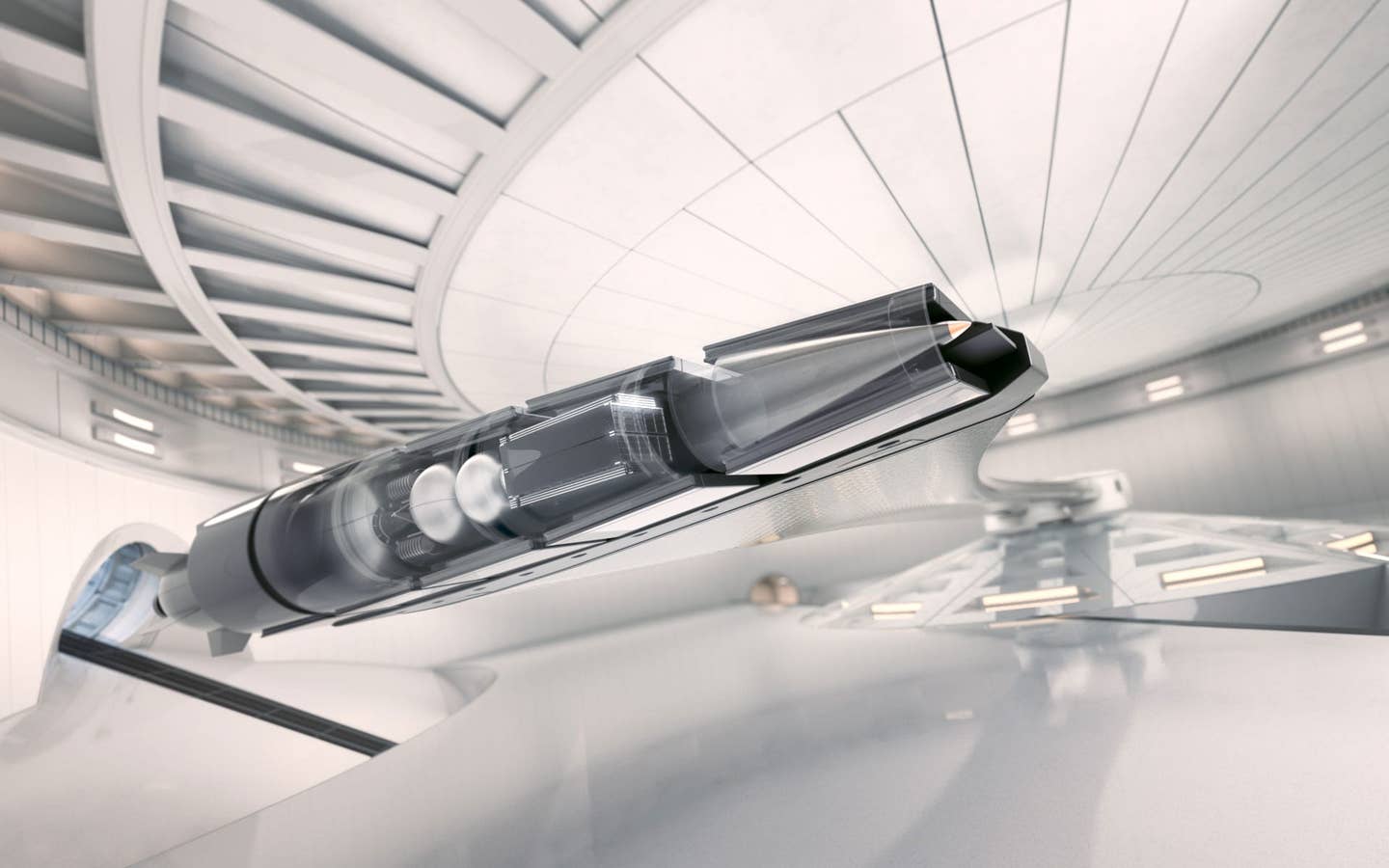
The company’s groundbreaking innovation is possible with modern materials and smaller electronic devices. High -strength carbon fiber and compact electronic system are essential for technology success.
“The latest electronic devices, materials, and simulation tools can easily adapt satellites to the exercise speed launch environment,” SpinLaunch explains on his website. This technology must withstand extreme conditions, such as vacuum and rapid acceleration in space.
One of the release of SpinLaunch in New Mexico shows excitement and accuracy. The engineer monitors the screen, and the launch scene is similar to the NASA mission control room scene. When the satellite leaves the launch barrel, it will occur very fast, so if it flashes, it will be easier to overlook.
SPINLAUNCH, established in 2014, has secured a lot of money and cooperates with major organizations such as NASA, Airbus, and Cornell University to use equipment for various tests. This technology has succeeded in the power of up to 10,000 GS, which is equivalent to 10,000 times the gravity pull of the earth, indicating its robustness.
If SpinLaunch technology is proved to be reliable and scalable, you can dramatically reduce the fuel required to launch satellite. For comparison, SpaceX’s Falcon 9 Rocket used more than £ 900,000 propellants for each launch in 2016. Since then, fuel efficiency may have been improved, but the huge amount of fuel required for conventional launch is still large.

The impact of the conventional rocket launching environment has been increased by monitoring. Each launch contributes to the depletion of the ozone layer that protects the life on the earth from the harmful radiation of the sun. SpinLaunch method provides potential solutions because the ozone layer can violate without damaging it.
Looking at the future, SpinLaunch will be built based on the initial success by developing coastal orbit launch sites. This next step is important to promote their technology and make them a substitute for the release of conventional rockets. “It has been proven to be a reliable system,” Yanny emphasized the promises and possibilities of the SpinLaunch approach.
In Singapore, the Space Technology Startup equatorial spaces system is one of the first numbers to open up this niche space. Singapore -based companies are developing a module -type low -cost launch car specially adjusted to send lightweight payloads to LEO. Similarly, it emphasizes cost, peace of mind, and sustainability, and its own sales points overlap with spin lane.

“The total address market for lower orbital launch from our research can increase to $ 150 million a year,” said Simon GWZDZ, founder and CEO of Equatorial Space Systems.
SpinLaunch technology can show a major change in the way of thinking and execution on satellite launch by combining environmental responsibilities and innovative engineering. As the company has been developing and testing the system, the future of satellite deployment may be clean, more efficient, and easier to access.
Other innovative satellite launch technology
Over the past decade, satellite launch technology has evolved significantly due to the need for expensive, efficient, and environmentally friendly methods. Some of the most innovative satellite launching technology developed in recent years are:
SPACEX’s Falcon 9: The most transformed rocket is the development of reusable rockets. SPACEX’s Falcon 9 has revolutionized the satellite launch industry by returning to the earth after the first stage of the rocket has expanded and reusing it with subsequent launches. This dramatically reduces the cost of the universe. BLUEORIGIN’s new shepherd: Similarly, Blue Origin has developed a reusable orbital material rocket. It has also proved that the company’s new Chepard can bring payload to the edge of the universe and land a reusable rocket stage for future flights.
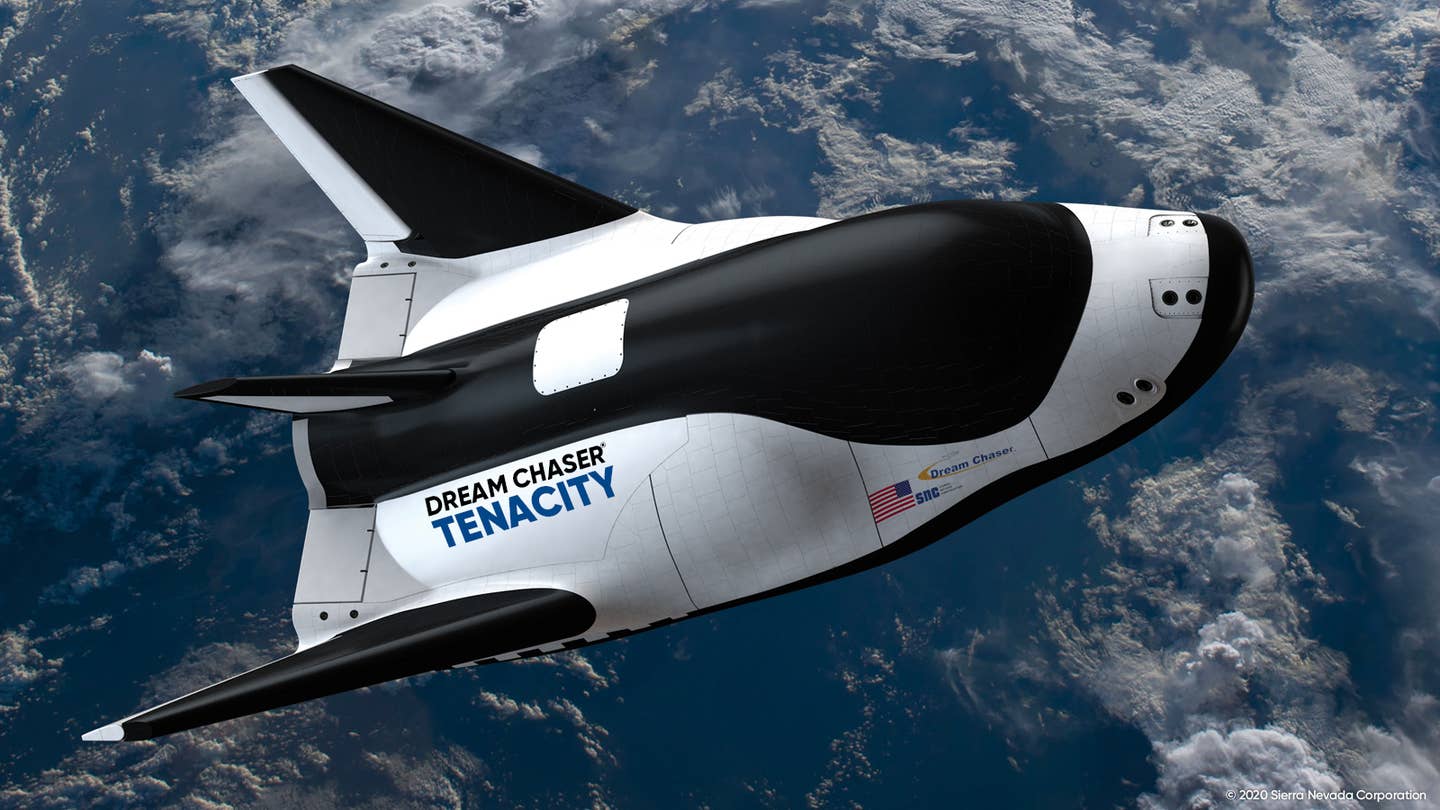
Rocket Lab’s Electron Rocket and Recovery Systemelectron Rocket, based in New Zealand, has developed an electronic rocket to the launch of a small satellite. It focuses on the quick and low cost access to the space for small payload. Rocket Lab is also working on partial reusable programs and tries to recover the first stage of the rocket via the aerial helicopter. SpacePlanes and Air-Raunched SystemSvirgin ORBIT’s launcher loan: Virgin Orbit’s launcher loan is a unique aircraft system to develop. A satellite from the corrected Boeing 747 aircraft. This method can cause firing from the runway, reducing flexibility and cost compared to the conventional ground -based rocket launch. The Dream Chaser of Sierranevadacorporation: The Dream Chaser is an astronaut developed to deliver cargo to the International Space Station (ISS). You can land on the conventional runway and provide reusable and flexible solutions for orbit transportation.

The 3D printed rocket (relativity space) relativity was pioneered the use of 3D printing in rocket production and created a Terran 1 rocket. The company claims that the entire rocket, including the engine, is printed 3D. This approach makes it faster and more flexible, reducing the costs related to conventional manufacturing. Electrical pumping with pumps such as lightweight astras and rocket labs focuses on small and light rockets such as Astra’s Rocket 3 and Rocket Lab’s Electron. Pump engine. These innovations make small satellite launching easier for a wide range of industries, such as communication and the earth observation, at a more affordable price.

Laser and microwave promotion system Systemswhile is still in the experiment stage, and researchers are working on laser promotion and microwave promotion technology. These systems can use a ground -based laser or microwave beam to promote spacecraft, reduce the need for onboard fuel, and provide more sustainable and more efficient means to reach tracks. I have sex. For example, SPACEX’s Starship and OneWeb satellite systems aim to launch thousands of small satellites to provide global Internet coverage. These satellites can be deployed in a batch and significantly reduce launch costs per satellite.

Space tags, orbital service moments and other companies are developing a space tag, a spacecraft designed to transport satellites from the first deployment location to the final orbital. These tags can reduce the amount of fuel that satellites needs to carry, making the launch more efficient and flexible. Hybrid and environmentally friendly rockets are increasingly interested in promoting hybrid rockets that combine solid fuel and liquid fuel to create more control. Efficient startup system. For example, Virgin Galactic Spaceshittwo uses a hybrid rocket engine. In addition, efforts to develop an environmentally friendly promotion system are on progress rather than reducing the launch of carbon dioxide launched.
These innovative technology shows a transition to a more cost -effective, flexible and sustainable way to launch satellites, and opens new opportunities for space exploration and commercial use.


