Oil and gas extraction is prohibited in Greenland for environmental reasons, and development in the mining sector is plagued by red tape and opposition from indigenous peoples.
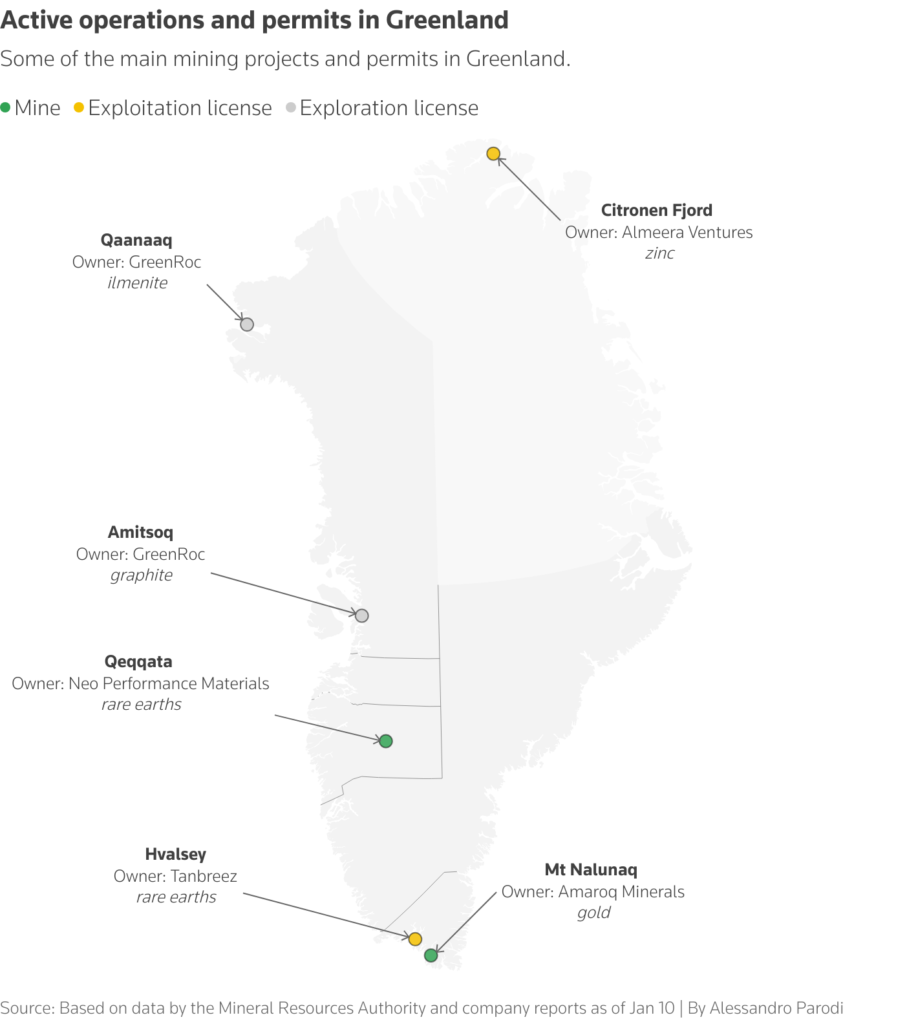
Below are details of Greenland’s major mineral deposits, based on data from the Greenland Mineral Resources Authority.
rare earth
Three of Greenland’s largest deposits are in South Gardar province.
Companies aiming to develop rare earth mines include Critical Metals, which purchased the Tamburrys deposit, Energy Transition Minerals, whose Quanasuit project has stalled amid legal disputes, and Neo Performance Materials. can be mentioned.
Rare earth elements are key to permanent magnets used in electric vehicles (EVs) and wind turbines.
graphite
Occurrences of graphite and graphite schist have been reported from many localities on the island.
GreenRoc has applied for an exploitation license to develop the Amitsoq graphite project.
Natural graphite is mainly used in EV batteries and steel manufacturing.
copper
According to the Department of Mineral Resources, most copper deposits have only undergone limited exploration activity.
Of particular interest are the unexplored areas in the northeast and central east of the island.
London-listed 80 Mile aims to develop the Disko Nussuak deposit, which contains copper, nickel, platinum and cobalt.
nickel
According to the Department of Mineral Resources, there are numerous signs of nickel accumulation.
Major mining company Anglo American obtained a five-year exploration license in western Greenland in mid-2019, and has been searching for nickel deposits.
zinc
Zinc is mainly found in the northern part of the country in geological formations spanning more than 2,500 km.
Companies have been seeking to develop the Citronenfjord zinc-lead project, which was touted as one of the world’s largest untapped zinc resources.
gold
The area with the most potential for gold is around the Sermiligarsk Fjord in the south of the country.
Amaroq Minerals launched a gold mine on Mount Narnak in the city of Kujarek last year.
diamond
Most small diamonds and largest stones are found in the western part of the island, but their presence in other areas may also be significant.
iron ore
Deposits are located in Isua in southern West Greenland, Ittiljarsk in central West Greenland, and in northwest Greenland along the Lauge Koch Kist.
titanium vanadium
Known deposits of titanium and vanadium are located in the southwest, east, and south.
Titanium is used for commercial, medical, and industrial purposes, and vanadium is primarily used in the production of special steel alloys. Vanadium pentoxide, the most important industrial vanadium compound, is used as a catalyst in the production of sulfuric acid.
tungsten
Tungsten, used for several industrial applications, occurs primarily in the central east and northeast of the country, with deposits being evaluated in the south and west.
uranium
In 2021, the left-wing Inuit Attakatigit Party banned uranium mining, effectively halting development of the Quanasut rare earths project, which contains uranium as a byproduct.

($1 = 7.2705 Danish Crowns)
(Editing by Elvira Luoma and Alessandro Parodi; Editing by Varun HK)


